Obesity is a big problem in the US. According to the CDC, 42% of adults and 19% of children are obese, which leads to diabetes, heart disease, and other chronic conditions. Many people struggle with traditional weight loss methods like diet and exercise alone.
Weight loss injections have become an effective medical solution for people who can’t lose weight through lifestyle changes alone. These injectable medications work by suppressing appetite, regulating blood sugar and metabolism, a scientifically proven way to lose weight safely.
In recent years, FDA-approved options like semaglutide (Wegovy), tirzepatide (Zepbound), semaglutide (Ozempic), and liraglutide (Saxenda) have gained popularity, showing 15-20% average weight loss in clinical studies. Real-world users have reported great results when combined with healthy diet and exercise plans.
With obesity rates rising, weight loss injections are becoming a key tool for doctors and patients looking for safe, effective, and sustainable weight management solutions. This guide will explain how they work, their effectiveness, cost, safety, and which one is best for you.
What Are Weight Loss Injections?
Weight loss injections are medically approved medications to help you lose weight safely and easily. Unlike diet pills or supplements, these injections target your metabolism and appetite using science-backed mechanisms. They are prescribed for people with a BMI above 30, or a BMI above 27 with weight-related health issues like diabetes or high blood pressure.
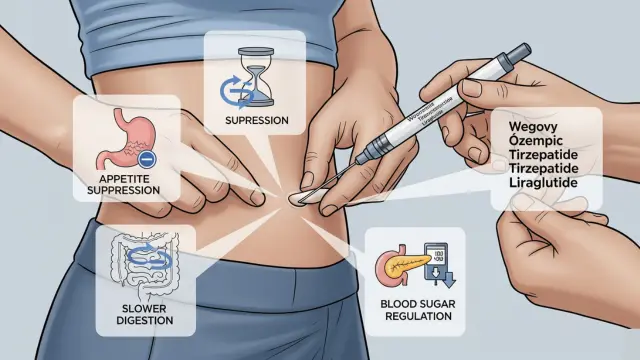
Most weight loss injections are GLP-1 receptor agonists. These medications:
- Suppress appetite, so you feel full faster
- Slow digestion, so you eat less naturally
- Regulate blood sugar and insulin to support fat burning
Popular FDA-approved injections are:
- Semaglutide (Wegovy) – Weekly injection with up to 20% body weight loss in trials
- Tirzepatide (Zepbound) – Dual GLP-1 and GIP receptor agonist with strong appetite suppression
- Liraglutide (Saxenda) – Daily injection for gradual, long-term weight loss
- Ozempic (Semaglutide) – Weekly injection, can support 15–18% body weight loss in clinical studies, widely used for appetite suppression and blood sugar control.
Why They’re Different from Pills or Diet Plans
Unlike oral supplements or fad diets, weight loss injections are clinically tested and FDA-approved. They work at the hormonal level, not just willpower or restrictive eating, so they’re more effective for people who struggle with traditional methods.
These injections are administered under medical supervision, usually via subcutaneous injection in the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm. They’re meant to be combined with lifestyle changes, including a balanced diet and exercise, for the best results.
How Do Weight Loss Injections Work?
Weight loss injections work by hitting the body’s hormones and metabolism, helping you lose weight faster than diet or exercise alone. Most of these injections are GLP-1 receptor agonists, which have been FDA-approved for weight loss.
How They Work
These injections work on the GLP-1 and GIP receptors in the brain and digestive system:
- Appetite Suppression: They tell the brain to feel full faster, so you eat less naturally.
- Slower Digestion: Food stays in your stomach longer, so you feel full for longer.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: By increasing insulin sensitivity, they prevent blood sugar spikes that lead to fat storage.
- Fat Metabolism Boost: Some injections like tirzepatide also help break down stored fat more efficiently.
Administration & Dosage
- Injection Sites: Abdomen, thigh, or upper arm
- Frequency:
- Semaglutide (Wegovy): Once a week
- Tirzepatide (Zepbound): Once a week
- Liraglutide (Saxenda): Daily
- Ozempic (Semaglutide): Weekly
- Professional Supervision: These medications are usually started under the guidance of a doctor who monitors weight, blood sugar, and side effects.
Combination with Lifestyle Changes
Weight loss injections are not magic bullets. For best results, they should be combined with:
- A balanced, low-calorie diet
- Regular exercise
- Healthy sleep and stress management
Do Weight Loss Injections Really Work?
Yes, weight loss injections can be super effective, but results vary depending on the medication, dosage, lifestyle, and individual health factors. They are clinically proven to help with significant weight loss when combined with diet and exercise.
Clinical Studies
- Semaglutide (Wegovy): A Study shows, participants lost an average of 15–20% of their body weight over 68 weeks.
- Tirzepatide (Zepbound): According to trials, up to 21% weight reduction at the highest doses.
- Liraglutide (Saxenda): Daily injections resulted in 5–10% weight loss in participants after one year.
- Ozempic (Semaglutide): Participants lost an average of 15–18% of their body weight over 68 weeks in clinical studies.
These results are way better than most diet programs or oral supplements, which is why weight loss injections are becoming popular among patients with obesity.
Real-Life Success Stories
- Many users have reported sustained weight loss and improvements in blood sugar, cholesterol, and blood pressure.
- For example, patients using Mounjaro (tirzepatide) with lifestyle changes have experienced long-term weight management with minimal weight rebound.
What You Need to Know
- Results vary – Genetics, diet/exercise adherence, and underlying health conditions affect outcomes.
- Medical supervision is required – Doctors monitor dosage, side effects, and overall health to maximize benefits safely.
Bottom Line: When used correctly and with a healthy lifestyle, weight loss injections are one of the most effective medical options for weight loss and weight management.
Different Types Of Weight Loss Injections
Weight loss injections come in various forms, each working differently to manage appetite, metabolism, and fat storage. Knowing the types and how they work will help you choose the right one under a doctor’s guidance.
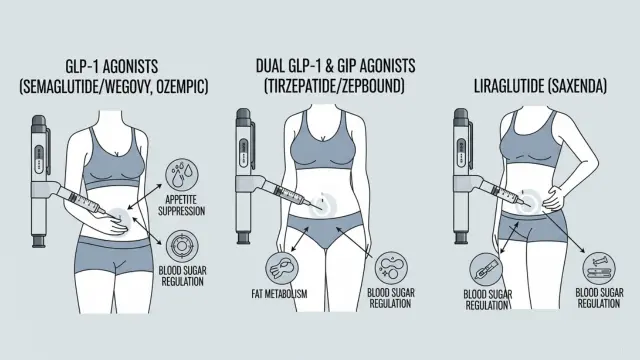
1. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
- Examples: Semaglutide (Wegovy), Ozempic (Semaglutide), Liraglutide (Saxenda)
- How They Work: Mimic the GLP-1 hormone in the body, which regulates appetite, slows digestion, and controls blood sugar.
- Effectiveness:
- Semaglutide (Wegovy): Participants lost an average of 15–20% of their body weight over 68 weeks.
- Ozempic (Semaglutide): Participants lost an average of 15–18% of their body weight over 68 weeks.
- Liraglutide (Saxenda): Daily injections resulted in 5–10% weight loss in participants after one year.
- Administration: Semaglutide and Ozempic are injected once a week, while Liraglutide is administered daily.
2. Dual GLP-1 & GIP Agonists
- Example: Tirzepatide (Zepbound / Mounjaro)
- How They Work: Combines GLP-1 and GIP hormone activity for better appetite suppression and fat metabolism.
- Effectiveness: Users in studies experienced up to 21% body weight reduction, often outperforming single-agonist medications.
- Administration: Weekly injection under medical supervision.
3. Other Injectable Options
- Emerging Medications: Some newer therapies and combination drugs are being researched for weight management.
- Note: Only FDA-approved injections should be used. Avoid unregulated or unverified products; they may be unsafe.
Apart from these weight loss injections, you can also try some natural weight loss methods such as Mitolyn.
Comparison Chart
| Injection Type | Brand Examples | Frequency | Avg. Weight Loss | FDA Approved | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLP-1 Agonist | Semaglutide (Wegovy), Ozempic (Semaglutide), Liraglutide (Saxenda) | Weekly / Weekly / Daily | 15–20% / 15–18% / 5–10% | Yes | Appetite suppression, blood sugar control |
| Dual Agonist | Tirzepatide (Zepbound / Mounjaro) | Weekly | Up to 21% | Yes | Strong appetite suppression, enhanced fat metabolism |
| Others | Emerging options | Varies | TBD | Pending | Experimental / under research |
Cost and Insurance Coverage of Weight Loss Injections
Weight loss injections can be pricy, but costs vary depending on the medication, dosage, and insurance. Knowing the cost and available programs is key before you start.
Average Cost of Popular Injections
- Semaglutide (Wegovy): $1,200–$1,500 per month without insurance
- Ozempic (Semaglutide): $1,100–$1,400 per month without insurance
- Tirzepatide (Zepbound / Mounjaro): $1,300–$1,600 per month
- Liraglutide (Saxenda): $1,000–$1,400 per month
Note: Prices reflect retail cost only and do not include doctor visits or supplies. Insurance coverage and manufacturer savings programs may reduce out-of-pocket costs.
Insurance Coverage
- Varies by Plan: Some insurance companies cover part or full FDA-approved weight loss injections if medically necessary.
- Requirements: Often coverage requires BMI, health conditions, and previous weight loss attempts.
- Tip: Call your insurance company to confirm coverage before you start.
Affordable Options & Savings Programs
- Manufacturer Savings Programs: Brands like Wegovy and Saxenda offer discount cards or copay assistance for eligible patients.
- Generic Alternatives: Most GLP-1 agonists don’t have generics yet; oral options like orlistat (Alli) are more budget-friendly.
- Discount Services: Platforms like GoodRx often have lower prices for eligible patients.
Bottom Line
Weight loss injections are a big investment, but insurance and manufacturer programs can make them more doable. Patients should explore all options and talk to their doctor to find the best combo of treatment and affordability.
FDA Approval & Safety Regulations
Weight loss injections are medically regulated to be safe and effective. Only FDA-approved medications should be used; unapproved alternatives can be dangerous and harmful.
FDA-Approved Weight Loss Injections
- Semaglutide (Wegovy): For adults with BMI ≥30 or BMI ≥27 with weight-related conditions
- Ozempic (Semaglutide): For adults with type 2 diabetes, also commonly used off-label for weight management
- Tirzepatide (Zepbound / Mounjaro): For type 2 diabetes with weight loss benefits; off-label use for obesity is being monitored
- Liraglutide (Saxenda): For chronic weight management in adults
Why FDA Approval Matters
- Clinical testing for safety and efficacy
- Dosage, side effects, and labeling
- Prevents unsafe, unverified products from entering the market
Regulatory Oversight & Guidelines
- Prescriptions must come from licensed healthcare providers
- Dosage and injection schedule monitored by medical professionals
- Regular check-ups, including blood sugar and liver function monitoring
Risks of Unapproved Injections
- Health hazards: Potentially dangerous ingredients, unknown side effects
- Ineffective results: No clinical testing means weight loss is not guaranteed
- Legal concerns: Selling or using unapproved products can be illegal
Using FDA-approved weight loss injections under medical supervision is key to safety and effectiveness. Avoid unregulated products and always follow your doctor’s instructions to get the best results with minimal risk.
Side Effects & Risks of Weight Loss Injections
While weight loss injections are effective, they carry potential side effects. Understanding these risks helps patients make informed decisions and use injections safely.
Common Side Effects
- Nausea and vomiting – usually mild and temporary, often easing after a few weeks
- Diarrhea or constipation – digestive changes are common as the body adjusts
- Injection site reactions – redness, itching, or swelling at the injection site
- Vision changes/eye discomfort – sometimes reported with Ozempic (Semaglutide)
Serious but Rare Risks
- Pancreatitis – inflammation of the pancreas, requiring immediate medical attention
- Gallbladder issues – gallstones or gallbladder inflammation in some patients
- Thyroid tumors – certain GLP-1 agonists may increase risk; regular monitoring is recommended
Who Should Avoid Weight Loss Injections
- Individuals with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma
- Those with severe gastrointestinal disorders
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- People taking medications that interact with GLP-1 or GIP agonists
Managing Side Effects
- Start with lower doses as prescribed to reduce nausea and digestive issues
- Hydrate and follow a balanced diet to manage gastrointestinal symptoms
- Report serious symptoms immediately to your healthcare provider, including any vision changes
Bottom Line
Most side effects are mild and manageable, but serious risks exist. Medical supervision and proper monitoring are essential to ensure safe and effective weight loss with injections. Always consult your doctor first.
Which Weight Loss Injection Is Best?
Choosing the best weight loss injection depends on your health goals, medical history, and lifestyle. There isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution, but comparing effectiveness, side effects, cost, and administration can help you make an informed decision.
| Injection | Average Weight Loss | Frequency | Common Side Effects | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Semaglutide (Wegovy) | 15–20% body weight | Weekly | Nausea, constipation, and injection site irritation | Patients seeking significant, gradual weight loss |
| Ozempic (Semaglutide) | 15–18% body weight | Weekly | Nausea, constipation, injection site irritation, and possible vision changes | Patients seeking effective weight loss with diabetes management or off-label weight management |
| Tirzepatide (Zepbound / Mounjaro) | Up to 21% | Weekly | Nausea, diarrhea, mild hypoglycemia | Patients who need strong appetite suppression and fat metabolism support |
| Liraglutide (Saxenda) | 5–10% | Daily | Nausea, vomiting, and injection site reactions | Patients preferring a daily dosage and moderate weight loss |
Things to Consider
- Effectiveness: Dual agonists like tirzepatide may lose a little more weight than single GLP-1 agonists.
- Frequency of Injection: Weekly options (Semaglutide, Tirzepatide) are more convenient than daily injections like Liraglutide.
- Side Effects: All injections will cause some digestive issues; serious risks are rare, but talk to your doctor about them.
- Cost & Insurance: Some are more expensive; insurance or manufacturer programs may impact your choice.
Our Advice
Start with an FDA-approved injection that fits your lifestyle and health profile. Regular check-ins will monitor weight loss, side effects, and overall health.
Bottom Line: The “best” injection is personalized. Your doctor will help you figure out which one balances effectiveness, safety, and convenience for you.
Conclusion
Weight loss injections are a game-changer for people struggling with obesity or weight-related health issues. Medications like Wegovy, Ozempic, Tirzepatide, and Liraglutide have proven results; patients lose significant weight when combined with a balanced diet and exercise.
These injections are not magic. Side effects like nausea, digestive issues, and injection site reactions are common, and rare but serious risks exist. Medical supervision is a must to ensure safe and effective use.
Choosing the right injection depends on your health profile, lifestyle, and treatment goals. Weekly options like Ozempic and Wegovy are convenient and effective, and daily injections like Liraglutide are for those who want gradual weight loss. Tirzepatide is for those who need higher effectiveness.
Ultimately, the most successful and long-term weight loss comes from combining FDA-approved injections with healthy eating, physical activity, and monitoring. Consulting a doctor is key to creating a plan that is safe and effective for you.
FAQs
What are the most popular weight loss injections?
The most commonly used FDA-approved injections are Wegovy (Semaglutide), Ozempic (Semaglutide), Tirzepatide (Zepbound / Mounjaro), and Liraglutide (Saxenda). Each works by controlling appetite, metabolism, and blood sugar.
How much weight can I expect to lose?
Clinical trials show:
Wegovy: 15–20% body weight over 68 weeks
Ozempic: 15–18% body weight over 68 weeks
Tirzepatide: Up to 21% body weight at the highest doses
Liraglutide: 5–10% body weight after one year
Are weight loss injections safe?
Yes, when used under a doctor’s supervision. Common side effects are nausea, diarrhea, constipation, and injection site irritation. Rare risks are pancreatitis, gallbladder issues, and thyroid tumors.
Can I use these injections if I don’t have diabetes?
Yes, some injections like Wegovy and Liraglutide are FDA-approved for weight management without diabetes. Ozempic is for type 2 diabetes, but often used off-label for weight loss.
How often do I need to inject these medications?
Wegovy and Ozempic: Weekly
Tirzepatide: Weekly
Liraglutide: Daily
Does insurance cover these injections?
Coverage varies. Some plans cover FDA-approved injections if medically necessary. Manufacturer savings programs and discount cards may also help reduce costs.
Can I combine injections with diet and exercise?
Yes. Weight loss injections work best with lifestyle changes, including a balanced diet, calorie control, and regular physical activity.
Who should avoid these injections?
People with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma, severe gastrointestinal disorders, pregnant or breastfeeding women, or those on medications that interact with GLP-1 or GIP agonists should avoid these injections unless advised by a doctor.

Recent Posts